Coir Logs for Erosion Control – Benefits, Specs & Installation
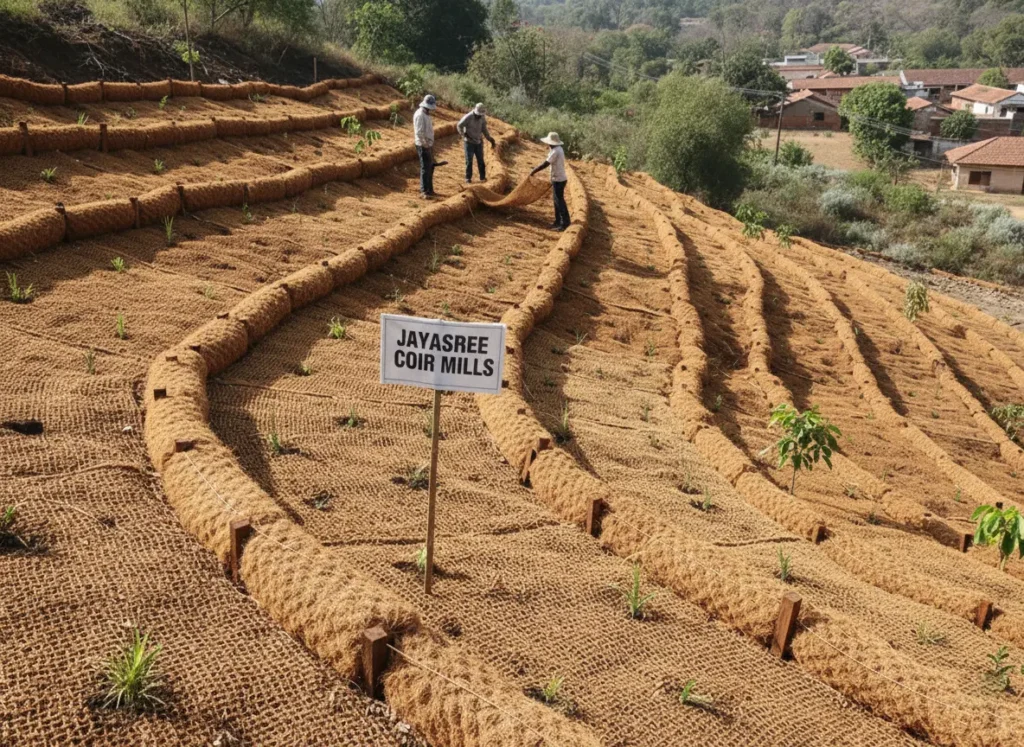

Coir logs are a proven solution for erosion control, addressing persistent environmental challenges faced by riverbanks, coastlines, and slopes worldwide. Traditional erosion control methods like concrete barriers and synthetic silt fences often solve one problem while creating another—pollution, habitat loss, and long-term waste. As industries and governments shift toward sustainable solutions, also known as coco logs, have emerged as an effective and eco-friendly alternative.
Coir logs are natural, cylindrical structures made from the fibrous husk of coconuts. They act as biodegradable barriers that stabilize soil, slow down water flow, and encourage vegetation growth in vulnerable areas. Their combination of durability and biodegradability makes them ideal for projects in shoreline restoration, riverbank protection, slope stabilization, and wetland rehabilitation.
This comprehensive guide explores everything about coir logs—from their scientific composition and environmental benefits to real-world applications, installation techniques, and global market trends. Whether you are an environmental engineer, landscape contractor, or sustainability professional, this article provides all the technical insights you need to understand why coir logs are redefining natural erosion control.
What Are Coir Logs?
Definition and Description
Coir logs are cylindrical erosion-control barriers made from densely packed coconut husk fibers enclosed in a coir netting. These natural fiber rolls are placed along shorelines, riverbanks, and slopes to slow water flow and trap sediment. Also known as coconut fiber logs or coco logs, they provide an environmentally friendly way to stabilize soil and encourage vegetation growth. Unlike synthetic wattles or plastic alternatives, they are completely biodegradable and naturally blend into the landscape. As they gradually decompose, the fibers release organic nutrients that enhance soil quality and support plant regrowth.
Unlike synthetic alternatives, coir logs are fully biodegradable. As they slowly break down, they enrich the soil with organic matter and support long-term habitat restoration. Their open fiber structure provides temporary stabilization while allowing water to flow and plants to establish. Coco logs are trusted for shoreline protection, streambank restoration, slope stabilization, wetland construction, and even as landscaping mulch for difficult-to-manage areas.
Key Characteristics:
100% natural coconut coir fiber (core) and coir twine netting (exterior)
Standard diameters: 20cm, 30cm and 40cm
Lengths: most commonly 1m. 2m, 3m and 6m with custom options available
Flexible and adaptable to various landscape contours
No plastics or synthetic chemicals
How Are Coco Logs Manufactured?
Coir logs are produced using a sustainable, multi-step process:
Coconut husks (a renewable byproduct) are collected and processed to remove dust and short fibers.
Long, unspun fibers are densely packed by machine or hand into tube-shaped sleeves of woven coir twine.
The coir netting is typically a 2″ x 2″ biodegradable mesh, designed for durability and easy rooting by plants.
Ends are securely tied or sealed with metal hog rings, ensuring the log maintains its shape during transport and installation.
The completed coir logs are then inspected for uniformity and strength, ready for use in various erosion control projects.
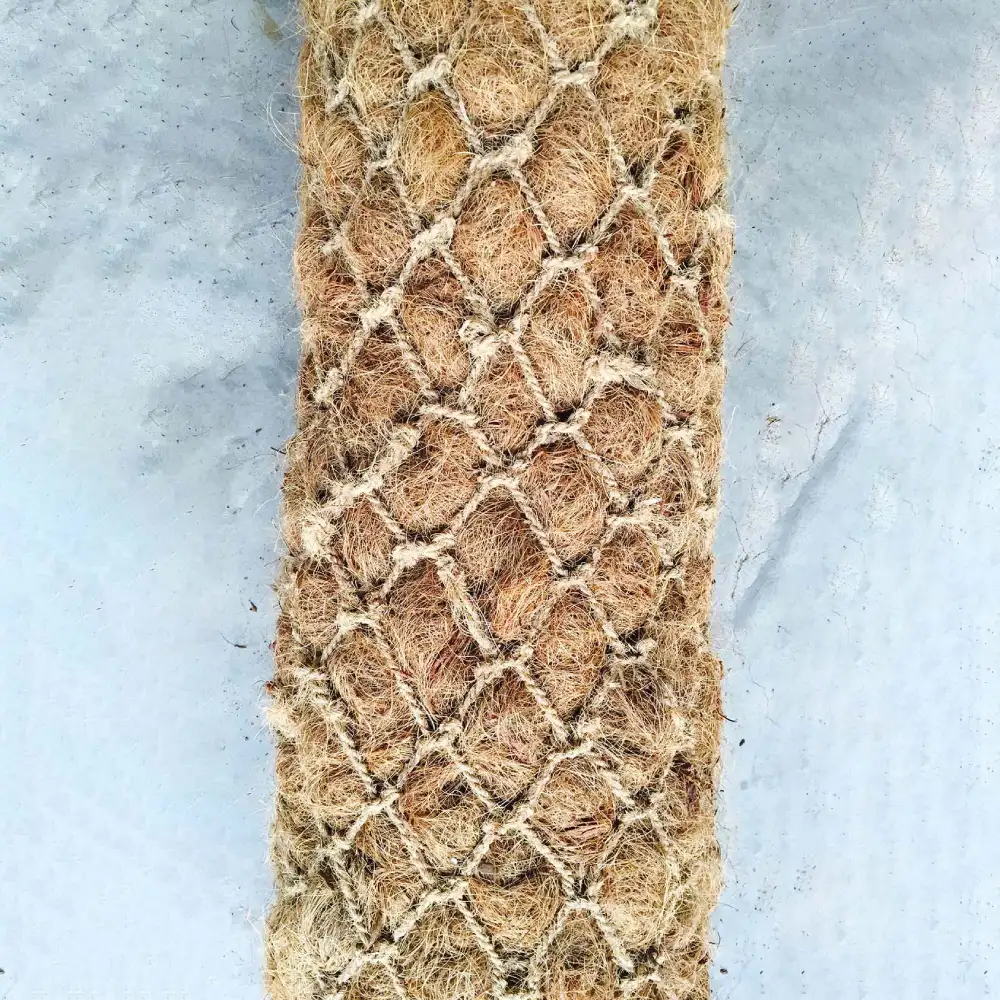

This manufacturing process results in a sturdy, all-natural product that can be installed with minimal environmental impact, supporting both immediate erosion control and the return of native plant life to degraded areas.
Specifications and Standards
Standard Sizes and Densities
Coir logs are available in multiple standard diameters and lengths to suit a variety of project needs and site conditions. The most common sizes used for erosion control and restoration projects are:
| Specification | Options |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 20 cm(8") – 40 cm(16") |
| Length | 1 m(3 ft) – 6 m(20ft) |
| Density | Standard Density/High Density [7 lbs/ft³ (112 kg/m³) or 9 lbs/ft³ (13.4 kg/m³)] |
| Outer Netting | Natural Coir Yarn/Poly net |
| Types | Round Log / Square Log / Pre-Drilled Log |
| Mesh Size | 5cm(2") X 5cm(2") |
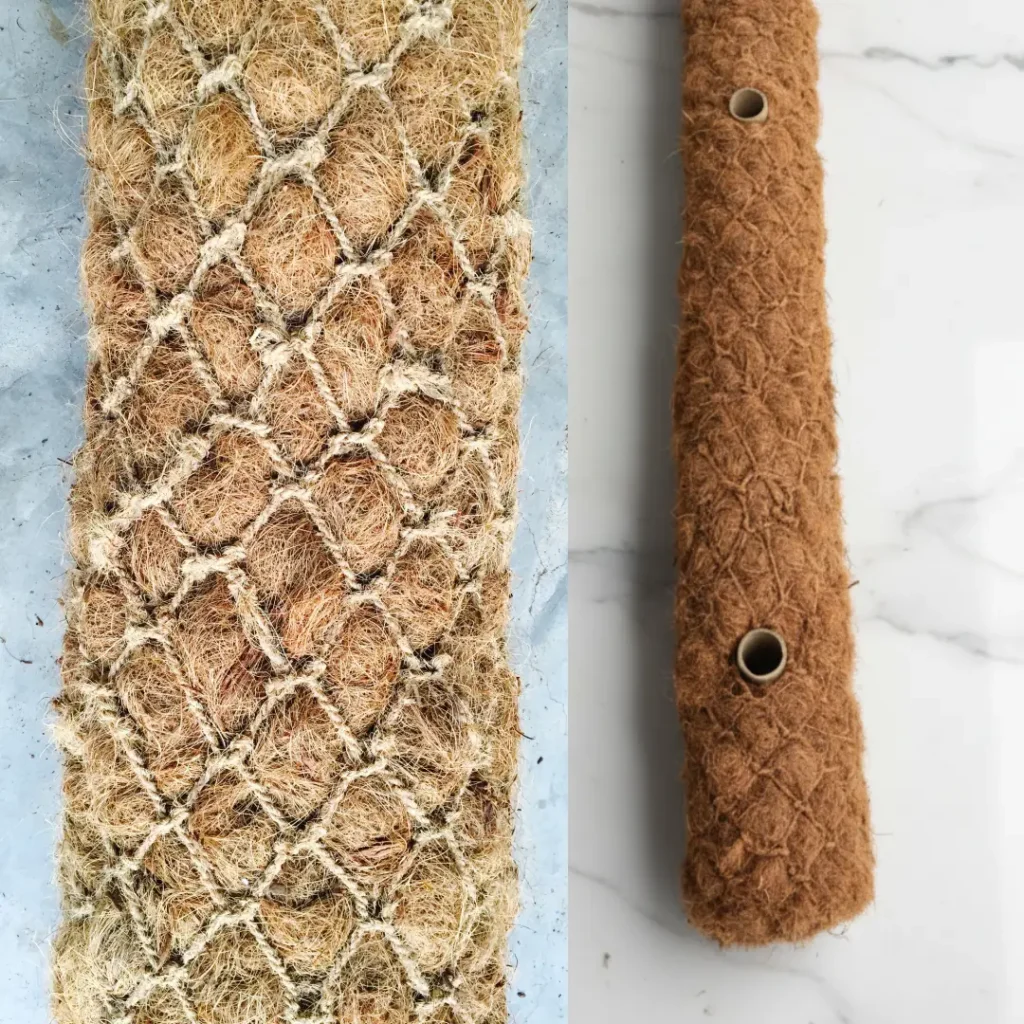

Diameters: 8″, 12″, 16″ (custom diameters available on request)
Lengths: Typically 1m , 2m, 3m, 6m per log; custom lengths also possible
Density: Standard logs are 7 lbs/ft³; high-density logs available at up to 9 lbs/ft³ for high flow or severe sites
Technical Details
Core Fill: 100% natural coconut coir fiber; unspun for maximum permeability and organic content.
Netting Size: Usually 2” x 2” biodegradable coir twine mesh, allowing for root penetration and rapid plant growth.
Durability: Designed to last 2–5 years in most field conditions, gradually biodegrading and enriching the soil.
Water Absorption: High; coir logs can absorb up to 150–200% of their own weight in water, aiding plant establishment and soil moisture retention.
Permeability: Allows water to flow through, trapping sediment but reducing erosive force.
Tip: For best results, always select log size and density based on flow velocity, project duration, and the degree of anticipated erosion. Consult with your supplier for recommendations for your specific site.
How Do Coir Logs Work?
Erosion Control Mechanisms
Coir logs provide immediate and natural stabilization by physically reinforcing shorelines, slopes, and streambanks against erosive forces. Their dense, fibrous structure acts as a semi-permeable barrier, slowing down water flow and allowing sediment to settle behind the log. This helps prevent the loss of valuable topsoil and keeps waterways cleaner.
Sediment Trapping: As water flows through and around the coir log, suspended particles are filtered out and retained, gradually building a new layer of soil behind the log.
Wave Energy Dissipation: The cylindrical shape and fibrous texture absorb wave and current energy, greatly reducing the impact of moving water on vulnerable soil.
Vegetation Support: The open mesh netting and organic fiber core create an ideal microclimate for plant roots. Seeds can be surface-sown or plugs inserted, with moisture retention from the log supporting rapid germination and root establishment.
With proper installation, coco logs can transform unstable, eroding banks into thriving, vegetated shorelines or slopes within one to two growing seasons.
Biodegradation and Soil Enrichment
Another key advantage is that coir logs biodegrade naturally over time, leaving no synthetic waste behind. As they slowly decompose over 2–5 years (depending on climate and site conditions):
Nutrient Release: Degrading coconut fibers release valuable organic material, improving soil fertility and supporting healthy vegetation.
Habitat Creation: As plants grow and mature through the log, a permanent, living root structure stabilizes the bank—eventually eliminating the need for the log itself.
Circle of Sustainability: The entire system supports a return to natural conditions, restoring habitats for wildlife and reducing future management needs.
Benefits of Coco Logs
Environmental Benefits
Coir logs offer unmatched environmental advantages compared to synthetic and other traditional erosion control options:
100% Biodegradable & Natural: Made entirely from coconut fiber and coir twine, coco logs break down safely over time, leaving no synthetic residue or microplastics in the environment.
Supports Aquatic and Riparian Life: Unlike plastics or treated materials, coir logs are safe for wildlife, fish, amphibians, and beneficial soil organisms.
Low Carbon Footprint: Coir is a renewable resource and a byproduct of the coconut industry, making use of otherwise discarded husks and supporting sustainable agriculture.
Zero Landfill Waste: When their job is done, coir logs compost naturally into the soil, contributing organic matter and nutrients that enhance the site’s long-term health.
Performance Benefits
Coir logs deliver practical, proven benefits for immediate stabilization and long-term project success:
Immediate Slope and Bank Stabilization: Coco logs provide robust protection as soon as they are installed, preventing further erosion before vegetation can take hold.
Reduces Maintenance and Reinstallation Needs: Their natural, gradual breakdown eliminates the need for costly removal or disposal.
Facilitates Vegetative Establishment: The moisture-retaining coir fiber core acts like a nursery bed, supporting seed germination and rapid root development for a permanent, living solution.
Adaptable to Varied Environments: Coir logs can be installed in gentle or steep slopes, slow or fast-moving water, coastal zones, and construction sites.
Economic and Practical Benefits
The practical and financial advantages of coir logs make them a favorite among engineers, ecologists, and landowners:
Lower Lifecycle Costs: While installation costs are comparable to alternative methods, the absence of synthetic cleanup, natural soil enhancement, and strong vegetation growth reduce long-term project expenses.
Eliminates Need for Removal: Coir logs don’t require removal at the end of their life cycle—they simply compost naturally.
Lightweight and Flexible: Easy to transport, handle, cut, and fit to curves or natural contours; installation is efficient, even in challenging terrain.
Proven and Trusted: Used worldwide in restoration and stabilization projects, with results backed by scientific case studies and government agencies.
Primary Applications of Coir Logs
Slope and Hill Stabilization
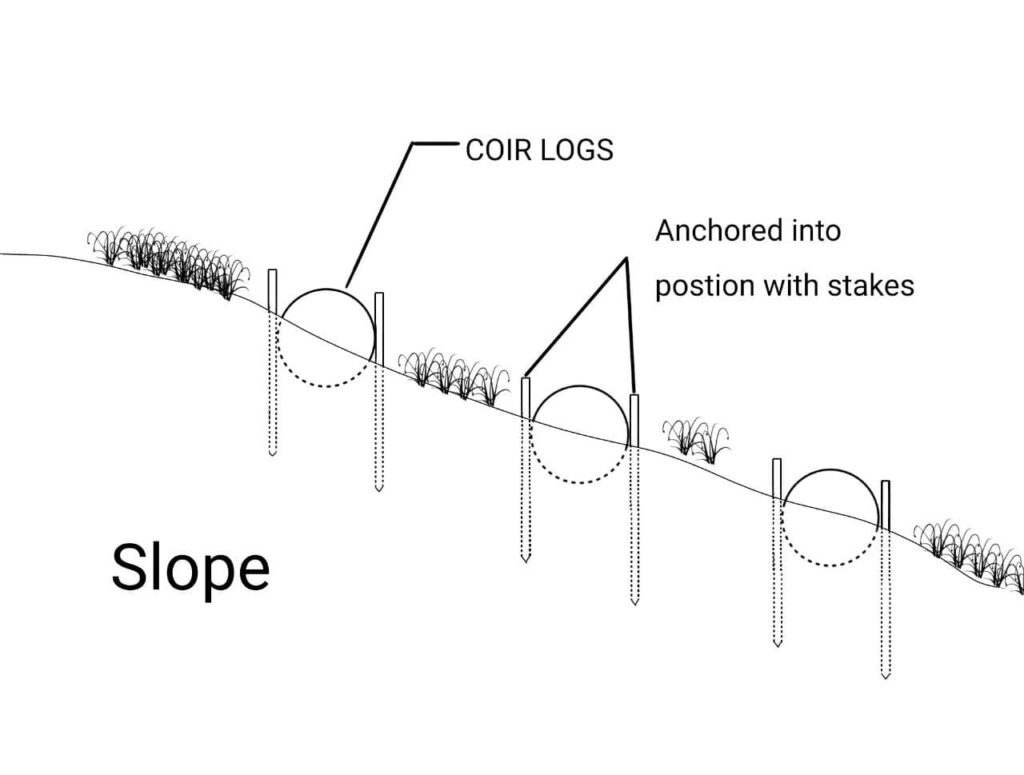
Coir logs are widely used for stabilizing steep slopes and embankments prone to soil erosion. By placing logs across the face of a slope, they slow runoff, trap sediment, and provide a supportive, moisture-rich environment where grass, native plants, or even trees can take root. This method is ideal for:
Roadway cut-slopes
Construction embankments
Garden terraces
Landslide-prone areas
Shoreline and Streambank Protection
Protecting streams, rivers, lakes, and coastal shorelines is one of the most common applications for coir logs. When installed along the water’s edge, they absorb wave and current energy, trap silt, and create a barrier that supports the growth of native riparian plants. Over time, the planted vegetation forms a living shoreline, preventing further erosion while restoring natural habitats.
Ideal for:
River and pond banks
Lake shorelines
Coastal restoration projects
Flood-prone zones
Wetland and Habitat Restoration
Coir logs play a key role in wetland restoration and wildlife habitat projects. Their natural materials and structure help establish transitional zones between water and land, creating conditions that support amphibians, birds, and beneficial insects. Wetlands stabilized with coco logs see faster plant establishment and increased ecological diversity.
Used in:
Constructed and restored wetlands
Buffer zones for wildlife habitats
Living fences for aquatic habitat creation
Construction and Infrastructure Sites
On construction sites and newly developed landscapes, coir logs are used as perimeter controls to manage runoff, trap sediment, and protect sensitive areas from disturbance. They’re flexible for temporary or permanent use and are a sustainable alternative to silt fences or straw wattles in:
Road, bridge, and culvert projects
Retention pond edges
Construction site sediment barriers
Scientific Research and Case Studies
Research on Effectiveness
Coir logs are backed by scientific studies and field data demonstrating their effectiveness in erosion control and environmental restoration.
Hydraulic Performance: Research has shown that high-density coir logs (up to 9 lbs/ft³) can withstand flow velocities of up to 3–4 ft/sec, making them suitable for moderate to high-energy streams and coastal zones.
Soil Retention: Field trials and laboratory tests indicate coir logs can reduce soil loss by up to 60% in critical locations, quickly trapping sediment and supporting rapid soil accretion behind the log.
Vegetative Growth: Studies highlight that seeds sown or plugs planted into coir logs demonstrate higher germination rates and more robust root systems, thanks to consistent moisture, organic matter, and protection provided by the coir matrix.
Biodegradation Rate: Multiple studies confirm coir logs decompose within 2–5 years, varying by local climate and hydrological conditions, leaving behind enriched soil and a stable, rooted plant community.
Case Examples
Lake Austin, Texas – Shoreline Restoration:
Over 14 years, coir logs helped reduce wave- and boat-induced erosion, stabilize sediment, and establish a healthy margin of native wetland plants, resulting in a thriving, resilient shoreline.
Pusu River, Malaysia – Riverbank Protection:
A field project using coir logs (combined with vetiver grass) achieved over 90% effectiveness in stabilizing a rapidly eroding riverbank, reducing soil loss, and promoting long-term root reinforcement.
Connecticut, USA – Hillside Slope and Habitat Restoration:
On a steep, 30-degree urban slope, coir logs enabled rapid establishment of vegetation and naturalized drainage, turning a previously unstable earthwork into a green, self-sustaining landscape in less than two years.
Wetland Projects:
Numerous restoration projects report faster, richer plant establishment, improved habitat complexity, and measurable improvements in water quality and bank stability with the use of coir logs compared to synthetic or inorganic alternatives.
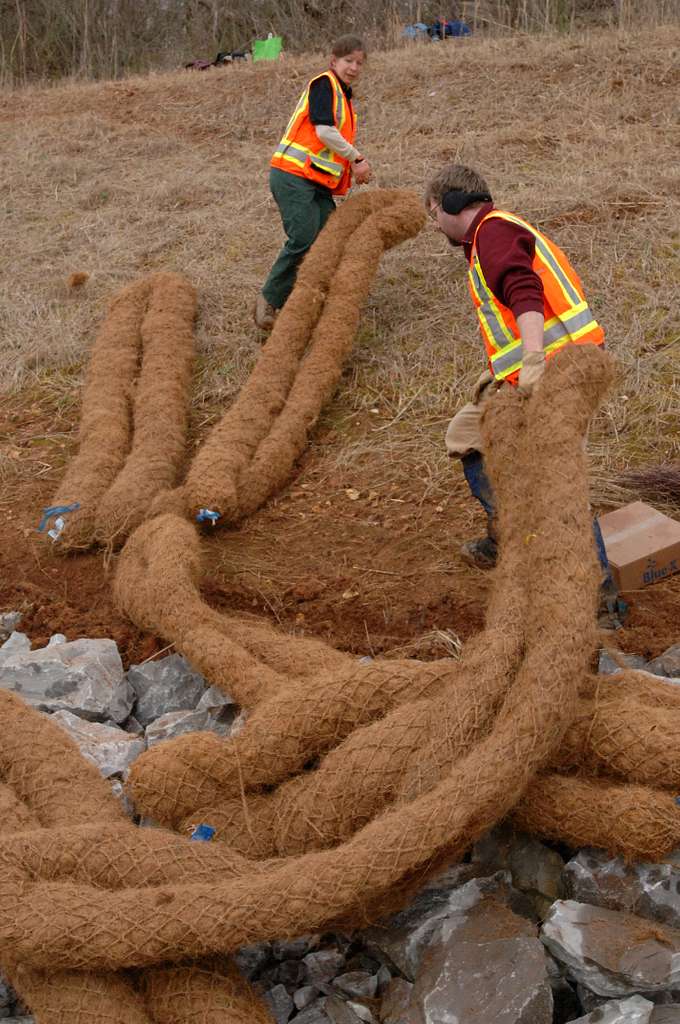

Installation Guidelines and Best Practices
Pre-Installation Planning
Proper planning ensures coir logs deliver maximum erosion control and ecological benefit. Begin by conducting a site assessment:
Evaluate flow conditions: Determine water velocity, depth, and seasonal fluctuation.
Survey soil and slope: Identify problem areas, bank angles, and soil composition.
Select log size and density: Match diameter and density to the site’s erosion risk (see specifications table).
Plan for vegetation: Identify native species that will thrive and complement the coir log system.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
Follow these steps for optimal coir log performance:
Site preparation: Clear debris, grade the slope, and lightly excavate a trench for partial log burial (about 1/3 the log’s diameter).
Placement: Lay the coir log horizontally along the designated bank, contour, or shoreline, ensuring tight contact with the soil.
End-to-end connections: For longer stretches, overlap or butt logs and tie together firmly with coir twine or natural rope.
Anchoring: Drive wooden or steel stakes through or on sides of the log at 3–5 foot intervals (or as manufacturer recommends), securing the log in place. Ensure stakes reach below the frost line in cold climates.
Backfill: Cover any exposed netting with soil for better moisture retention and plant growth.
Vegetation integration: Surface-sow native seeds or insert plant plugs directly into the log mesh. Water thoroughly, especially in the initial establishment phase.
Vegetation Integration
Plant Selection: Choose native grasses, rushes, sedges, or wetland plants adapted to moisture and climate.
Seeding Methods: Broadcast seed over the log or use cuttings/plugs inserted into the mesh.
Root Establishment: Coir fiber’s moisture retention supports rapid germination and strong root growth.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Insufficient staking or anchoring: Leads to displacement during high water.
Poor end treatment: Gaps between logs can allow erosion; always overlap or butt and tie logs.
Inadequate burial or compaction: Exposed logs dry out, shift, or underperform.
Wrong density selection: Low-density logs may not withstand high-energy environments—match product to project!
Coir Logs vs Alternative Erosion Control Methods
When selecting the best erosion control solution, it’s important to consider not just performance but also ecological impact, ease of installation, and long-term outcomes. Coir logs stand out for projects where sustainability and rapid site rehabilitation matter most.
Coir Logs vs Rock Riprap
Environmental Impact: Coir logs are fully biodegradable and improve soil health as they break down. Rock riprap is permanent but provides little benefit to soil or plant life and can alter natural water flow, potentially harming habitat.
Support for Vegetation: Coir logs encourage rapid and dense plant growth, allowing a living root matrix to develop for permanent stabilization. Rock riprap can hinder plant establishment, resulting in a less natural appearance and slower ecological recovery.
Aesthetics and Integration: Coir logs blend seamlessly with the natural landscape and become part of it over time. Riprap, by contrast, can appear artificial and visually intrusive along natural shorelines and banks.
Installation: Coir logs are lightweight, easy to transport, and can be installed by hand—ideal for sensitive or remote sites. Riprap requires heavy machinery, skilled labor, and greater site disturbance.
Coir Logs vs Synthetic Wattles
Eco-Friendliness: Coir logs decompose fully, leaving no synthetic residues, and their material is sourced from agricultural byproducts. Synthetic wattles may persist in the environment and eventually contribute to microplastic pollution.
Vegetative Establishment: Coir’s fibrous structure supports seed germination and root development far more than most synthetic alternatives, resulting in faster site recovery and improved erosion control.
Long-Term Site Health: As coir logs break down, they contribute organic matter to the soil—enhancing its fertility for years ahead. Synthetic wattles provide no such benefit and often require post-project removal.
Maintenance: Both options require little maintenance, but coir’s ability to blend into the landscape as it degrades means ongoing interventions are minimized.

Coir Logs vs Synthetic Materials
Photo showing a lush, vegetated shoreline or hillside where coir logs have disappeared into the landscape,
versus a site dominated by rocks or synthetic material
Conclusion for Project Selection:
Choose coir logs when sustainability, habitat recovery, and soil improvement are project priorities. They are particularly ideal for natural shoreline restoration, wetland construction, and environmentally sensitive landscapes where integration and ecological outcomes matter.
Cost Guide and Purchasing Tips
Factors Influencing Cost
Diameter & density: Larger and denser logs provide more protection and durability, but cost more.
Order quantity: Bulk orders typically secure discounted rates.
Customization: Special sizes, pre-vegetated logs, or unique netting options can influence pricing.
Shipping & logistics: Transportation costs depend on project site and supplier proximity.
Assessing Project ROI
Coir logs offer significant long-term cost advantages:
No removal costs: As they biodegrade, coir logs eliminate the need and expense of synthetic product cleanup.
Reduced maintenance: Enhanced vegetation growth means lower maintenance and less need for replacement.
Habitat and soil enhancement: Long-term soil improvement leads to greater ecosystem stability and fewer replantings.
Compliance: Projects using biodegradable, natural products may qualify for environmental grants or easier regulatory approval.
Buying Criteria
To ensure you’re purchasing high-quality coir logs, consider:
Manufacturer reputation: Choose established companies with reliable supply chains and documented technical standards.
Certifications: Look for logs ensuring consistent performance and durability.
Material quality: Inspect core fiber composition and netting quality; avoid low-quality imports with excess debris or weak mesh.
Customer service: Responsive support and clear warranty or guarantee provisions can be critical for larger projects.
Lead times: Assess supplier delivery schedules to align with project timelines, especially for bulk or custom orders.
Tip: Request product data sheets and third-party test reports for assurance on performance and compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are answers to the most common questions about coir logs for erosion control:
Q1: How long do coir logs last in the field?
Coir logs typically last 2–5 years, depending on site conditions, water flow, and climate. They gradually biodegrade, enriching the soil and supporting permanent vegetation.
Q2: Can coir logs be used in saltwater environments?
Yes. Coir logs are naturally resistant to decay and are suitable for both freshwater and saltwater applications, including coastlines and tidal zones.
Q3: Do coir logs require removal after use?
No. Coir logs are fully biodegradable; there is no need for removal—they safely compost into the environment as vegetation becomes established.
Q4: Which diameter and density should I choose for my project?
Select diameter based on bank height, site exposure, and flow velocity. Use high-density logs (145 kg/m³; 9 lbs/ft³) with diameters of 40–50 cm (16–20") for severe erosion, larger rivers, and high-energy sites. For smaller streams and garden slopes, standard sizes—20–30 cm (9–12") diameter, 112 kg/m³ (7 lbs/ft³)—are appropriate.
Q5: Can I plant vegetation directly into coir logs?
Yes. Coir logs support seed broadcast or direct planting of native plant plugs. Their moisture retention and open mesh structure make them ideal for rapid plant establishment.
Q6: Are coir logs safe for wildlife and aquatic habitats?
Absolutely. Coir logs are non-toxic, natural, and habitat-friendly, supporting the return of fish, amphibians, birds, and beneficial insects.
Q7: Are coir logs suitable for steep slopes?
Yes. When correctly installed and anchored, coir logs stabilize slopes up to 1:1 grade. For steeper or highly eroded areas, consult an engineer or supplier.
Q8: What maintenance do coir logs require?
Minimal. Initial inspection after installation is recommended, plus periodic checks during the first year, especially after major storms.
Q9: Are custom sizes or pre-vegetated logs available?
Yes. Many manufacturers offer custom diameters, lengths, densities, and pre-vegetated, pre-drilled options tailored to specific projects.
Environmental Impact and Market Trends
Sustainability Analysis
Coir logs represent one of the most sustainable solutions available for erosion control and ecological restoration.
Renewable material: Coconut coir is a byproduct of the coconut industry, using agricultural waste that would otherwise be discarded. This circular approach maximizes resource utility while minimizing environmental footprint.
Zero synthetic chemicals: Coir logs contain no plastics or additives, meaning no pollution or microplastic residues are left behind as they decompose.
Full biodegradability: After performing their function, coir logs naturally break down into the soil, enhancing organic content, improving moisture retention, and supporting healthy plant growth.
Supports local communities: Coir production creates jobs in rural areas, and global demand for green restoration products encourages responsible farming and fair trade practices.
Restores habitat: By supporting rapid vegetation and habitat diversity, coir logs play a role in bringing back native species, restoring water quality, and rebuilding ecological resilience in damaged areas.
Market Growth
Demand for eco-friendly erosion control products like coir logs is surging worldwide, driven by sustainability goals and stricter regulations.
The global market for coconut coir products is forecasted to nearly double by 2030, with increasing adoption in construction, landscaping, water management, and environmental projects.
Urban planners, civil engineers, and conservationists are moving away from synthetic and hardscape solutions, favoring natural products that restore instead of replace.
Public and private sector projects now frequently specify biodegradable, soil-building materials as part of regulatory requirements for green infrastructure and climate adaptation.
Government incentives, environmental grant programs, and rising consumer and developer awareness are further accelerating growth for coir and related natural fiber products.
Choosing coir logs aligns with global movements toward ecological restoration and climate resilience. Their proven effectiveness, green credentials, and ability to restore natural function make them an ideal choice for modern erosion control.
In conclusion, coir logs provide a sustainable, effective, and environmentally sound solution for erosion control across a wide range of landscapes. By combining natural fiber strength with biodegradability, they protect the environment while supporting long-term vegetation growth. Therefore, whether the project involves riverbank stabilization, coastal defense, or slope restoration, coir logs remain one of the most practical and proven options available today.
Unlike synthetic alternatives, coir logs blend naturally, break down safely, and enrich the landscapes they protect—leaving no waste, no harm, and a legacy of restored habitat. Their versatility, ease of installation, and proven performance make them the trusted choice for engineers, ecologists, landscapers, and landowners seeking both immediate results and lasting regeneration.
Ready to get started with coir logs for your project?
Choose coir logs—the sustainable, effective answer to erosion that helps both your land and the planet thrive
